What Is Hyperpigmentation?: Causes & Best Treatments Options For Your Skin
What Is Hyperpigmentation?: Causes & Best Treatments Options For Your Skin
Our skin endures a lot of inconveniences on a daily basis. From acne, scarring and hormone fluctuations to external pollutants like the sun and wind, we should be thankful that our skin is resilient. However, sometimes we have to pay a small price for our complexion’s defense system – namely, hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation is a byproduct of melanin overproduction that develops in concentrated areas on your complexion to cope with minor skin traumas, such as inflammation, hormone fluctuations and direct sun exposure. Genetics also determine whether (and how prominently) hyperpigmentation develops on your skin. It’s possible to be born with hyperpigmentation or a higher likelihood of developing dark spots develop throughout your complexion as you age – no matter how well you care for your skin.
While hyperpigmentation is not necessarily permanent, it can be a stubborn, complex skin condition to treat. Discovering the right skincare routine, products and cosmetic treatments for your skin type – along with healthy lifestyle habits - is the best way to reduce or prevent hyperpigmentation and see a drastic improvement in your complexion’s tone and radiance.

Expert Tip: Zensa Healing Cream contains medicinal-grade calendula oil and grapefruit essential oil. These ingredients are rich in vitamin C, an antioxidant that inhibits melanin production to reduce hyperpigmentation, even skin tone and brighten your complexion. In addition to treating existing hyperpigmentation, Zensa Healing Cream also contains anti-inflammatory ingredients like sunflower seed oil and avocado oil to boost collagen production and reduce acne and eczema flare-ups or similar skin conditions. These antioxidant-rich plant oils can help curb post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation to prevent dark spots from forming. Apply Zensa Healing Cream twice daily on the affected area for the best results.
Read on to learn more about types of hyperpigmentation, how they develop, causes of hyperpigmentation and treatment options to get rid of increased skin pigmentation.

What is Hyperpigmentation?
Hyperpigmentation is the term used to describe darkened patches of skin, resulting from melanin overproduction in concentrated areas of the body. Otherwise known as dark spots, age spots, liver spots or sun spots, hyperpigmentation refers to any increased pigmentation on the body – whether it’s small spots on your face and neck or large areas of darkened skin. Hyperpigmentation is like a pigmented, protective cushion that forms underneath the skin to defend itself against perceived threats like inflammation, sun exposure and hormone imbalances.
While it may trigger some insecurities, hyperpigmentation generally does not pose harm to your health or indicate some underlying medical condition. Hyperpigmentation is almost exclusively a cosmetic concern. However, darkened skin patches you believe to be hyperpigmentation could potentially be a sign of a more dangerous condition like skin cancer growth. Always go to your dermatologist or primary doctor if you see any new dark spots or signs of increased pigmentation on patches of your skin – especially if they don’t seem to be fading or going away on their own. Book annual skin exams out of an abundance of caution. It’s always better to be safe rather than sorry.
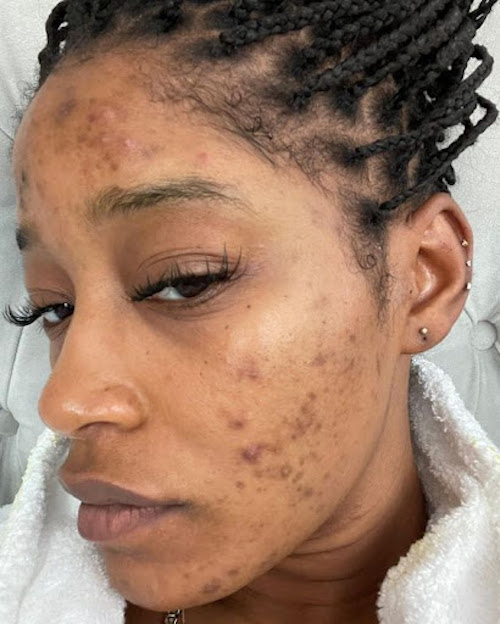
Credit: Ayanna Denise/Pinterest
Types of Hyperpigmentation
While hyperpigmentation is used as a catch-all term for darkened skin patches, there are three distinct types of hyperpigmentation. Each type of hyperpigmentation has its own set of potential causes, treatment options and prevention methods. Understanding the type you’re experiencing is essential to get to the root cause of your hyperpigmented skin and will aid you in adjusting your skincare regimen to help restore a more even-toned complexion. The three main types of hyperpigmentation include:
-
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation
-
Melasma
-
Age Spots (Sun Spots)
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation:
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs when your skin produces extra melanin as a result of inflammation or injury. These minor skin traumas are responsible for this most common type of hyperpigmentation. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is often caused by acne, eczema, razor bumps, rashes, burns, rosacea, psoriasis, bug bites, infections or allergic reactions. Dark spots associated with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation can appear as various shades of tan, brown or blue-gray patches on the skin. Post-inflammatory can occur at any age and is equally likely to develop in men and women. However, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation is more likely to form in those with dark or black skin than in individuals with lighter complexions.
Most cases of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation will eventually fade on their own – even without a designated treatment plan. However, it is almost always necessary to alter your skincare routine to treat post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation effectively. You might also want to consider specialty skin acids or cosmetic treatment options like microneedling or chemical peels if you want your post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation to fade relatively quickly (under 12 months) and eventually go away (even if not permanently).
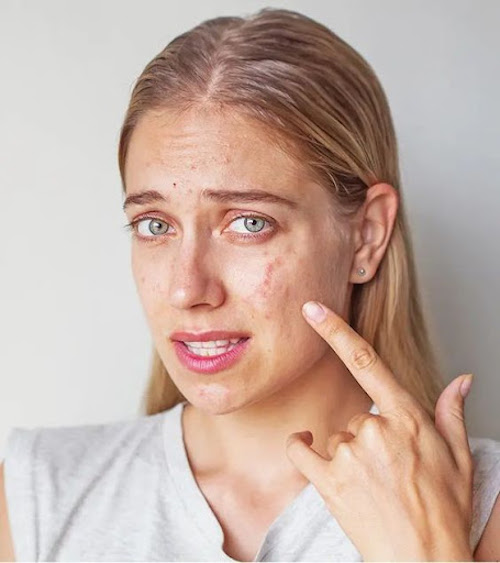

Credit: Stylecraze/Pinterest
Melasma:
Melasma is a type of hyperpigmentation that is most often associated with pregnancy and female hormone fluctuations (namely estrogen and progesterone) as a side effect of taking birth control pills, stress or hormone therapy. The condition is so closely linked with expecting mothers that melasma is sometimes called “the mask of pregnancy.” Over 90% of individuals who experience melasma are women, according to the American Academy of Dermatology. While less common, other causes of melasma include sunlight and other exposure to UV rays (such as from tanning beds), thyroid diseases and nutritional deficiencies, especially diets lacking in vitamin B12, vitamin D, folic acid and iron. Studies have linked melasma to poor liver function, vitamin B12 deficiency and iron deficiency anemia.
Symptoms of melasma include increased pigmentation on different parts of the face, such as the cheeks, chin, forehead, nose and above the upper lip. Melasma can develop on the jawline, neck or arms, too. Direct exposure to sunlight can make melasma patches more noticeable. This condition is more common among individuals with medium to dark skin tones.
Melasma should never feel itchy or painful. Contact your doctor if you’re experiencing discomfort around discoloured skin patches to determine whether you need medical attention, not just a cosmetic intervention. If pregnancy is triggering your hyperpigmentation, the melasma patches should go away shortly after giving birth. When treating melasma with other root causes, you might need to switch up your skincare routine to include ingredients known for reducing hyperpigmentation, modify your diet and lifestyle habits or consider cosmetic treatments like chemical peels and microneedling.
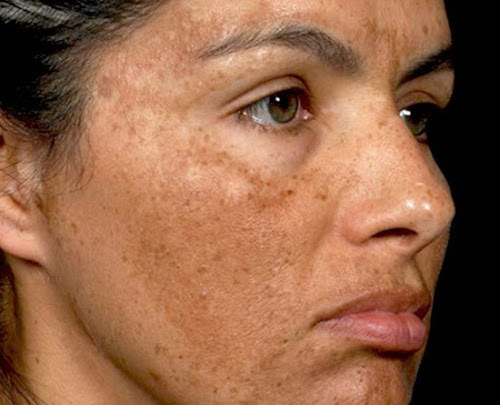
Credit: The Pretty Pimple/Pinterest
Age Spots (Sun Spots):
Age spots – otherwise called sun spots or liver spots – are flat freckles on the skin caused by excessive melanin production. This type of hyperpigmentation typically manifests as light to dark brown, gray or black spots on your face, neck, upper back, shoulders, chest, forearms and the back of your hands. Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to develop hyperpigmented clusters on their skin as they age – regardless of their lifestyle habits. When age spots are hereditary, they can begin to appear as early as childhood or during one’s adolescent years on the skin. The most common cause of age spots is exposure to UV rays, which can occur from direct sunlight, tanning beds and gel LED lamps. Age spots typically develop on areas that have the most unprotected contact with the sun or devices that offer considerable UV ray exposure. While your doctor should always do a skin check when new dark spots appear, remember that age spots are a cosmetic concern and are not cancerous. Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every morning to prevent sun damage and age spots from forming.
Different skincare remedies, prescription treatments and procedures, including dermabrasion, microdermabrasion and chemical peels, are known treatment options for effectively fading age spot-related hyperpigmentation.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
-
Acne
-
Cuts, Scrapes, Burns
-
Rashes, Infections, Allergic Reactions
-
Eczema
-
Sunlight
-
UV Ray Exposure (Tanning Beds, Gel LED Lamps, etc.)
-
Adrenal Disorders (e.g. Addison’s Disease)
-
Hormonal Changes/Imbalances
-
Nutrient/Vitamin Deficiencies (Namely Vitamin B12 and Folic Acid)
-
Skin Aging
-
Pregnancy
-
Thyroid Disorders
-
Genetics
-
Psoriasis
-
Rosacea
-
Medications that Cause Light Sensitivity

Credit: Natascha Lindemann/Pinterest
Hyperpigmentation Treatment Options
Treating hyperpigmentation requires a long-term, holistic approach. There’s no quick fix or short-term solution for getting rid of hyperpigmentation – no matter the underlying cause. While many cases of hyperpigmentation (especially PIH) will fade on their own, this process can take anywhere from 6-24 months without direct intervention. To treat hyperpigmentation effectively (and relatively quickly), consider treatment options that require adherence to a well-curated, diligent skincare routine and/or a series of professional cosmetic treatments. The right hyperpigmentation treatment option for your complexion will depend on the type of hyperpigmentation, its root cause, your skin type and the severity of your specific case.

How To Get Rid of Hyperpigmentation: Skincare
When choosing the best skincare products to help treat hyperpigmentation, look for ingredients known for their skin-lightening and complexion-brightening benefits. These substances work by decreasing excess melanin present on the skin, inhibiting melanin production through suppressing tyrosinase functioning (the enzyme responsible for catalyzing melanin development) or stimulating cellular turnover to break up melanin clusters for a more even skin tone. Most of these products can be found in over-the-counter (OTC) skincare formulas or as standalone serums. However, there are certain maximum-strength versions of popular ingredients (namely Hydroquinone and Retinoids) that require a prescription.
Always speak with your dermatologist before adding one of these ingredients to your daily regimen. Seeking expert advice is particularly important if you have dark or black skin (Fitzpatrick Types 4-6). Individuals with brown to black skin tones often are more susceptible to hyperpigmentation triggers that cause increased pigmentation. If already present, hyperpigmentation also tends to be more severe on dark skin tones and takes longer to treat compared to individuals with fairer complexions. Every ingredient listed below is recommended for all skin tones.
-
Hydroquinone
-
Arbutin
-
Licorice Root Extract
-
Azelaic Acid
-
Kojic Acid
-
Vitamin C
-
Retinoids (Topical Vitamin A)
-
Niacinamide
-
Tranexamic Acid
-
Glycolic Acid
-
Lactic Acid
-
Mandelic Acid
-
Salicylic Acid
-
Sunscreen

Hydroquinone is a skin-lightening agent that bleaches your skin by decreasing the concentration of melanocytes (the cells responsible for melanin production) present. Due to some controversy over the ingredient, hydroquinone is no longer available OTC and can be acquired by prescription only. Be cautious about using hydroquinone if you have dry, sensitive or darker skin. It can further dry out or irritate your complexion if you don’t have normal or oily skin. Hydroquinone can have the opposite intended effect on dark skin tones and worsen hyperpigmentation. Some natural alternatives to hydroquinone include arbutin (extracted from bearberry, mulberry or pomegranate) and licorice root extract. Both of these ingredients also inhibit melanin production without questionable side effects and can have increased efficacy to treat hyperpigmentation when combined with niacinamide and vitamin C.
Azelaic Acid is a tyrosinase inhibitor (decreases melanin production). It contains antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties to fight acne, offering the combined benefit of also preventing PIH. Azelaic Acid is suitable for sensitive skin and is an effective, milder alternative to salicylic acid for individuals with rosacea, acne-prone complexions or anyone with a compromised skin barrier.
Kojic Acid suppresses melanin production, another tyrosinase inhibitor, and is known to visibly improve hyperpigmentation (melasma, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and sun spots) within around 2 weeks. It works extremely quickly compared to other effective treatments for hyperpigmentation, such as retinol (6-8 weeks) or tranexamic acid (8-12 weeks). However, kojic acid can irritate sensitive skin and make your skin prone to sun damage, so always pair it with sunscreen when completing your morning skincare routine.

Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that offers the dual benefit of helping to fade dark spots and brighten your skin. It also blocks the enzyme responsible for melanin production. Combined with its high antioxidant content, vitamin C’s collagen-stimulating benefits promote cellular turnover to break up the existing melanin clusters and resurface your complexion with a fresh layer of more even-toned skin. Here’s everything to know about the benefits of vitamin C for your skin and the best (& worst) ingredients to combine with the antioxidant.
Retinoids (vitamin A derivatives) provide a three-prong approach to reducing and preventing hyperpigmentation. It inhibits tyrosinase production, fights acne and boosts collagen production. Some benefits of retinoids include halting excess melanin production, preventing new PIH patches from forming and encouraging cellular turnover to consistently resurface the skin. While highly effective, retinoids’ exfoliating benefits can irritate your complexion if you have more sensitive skin. Always use it at night, and follow up with sunscreen the following morning.
Niacinamide, otherwise known as vitamin B3, has been clinically proven to reduce visible hyperpigmentation in as little as 4 weeks. The water-soluble ingredient reduces inflammation, fights acne, protects against sun damage and boosts collagen production to increase cellular turnover. Niacinamide offers a dual benefit: It helps fade existing dark patches and prevents more post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation or new age spots from forming.'
Exfoliating acids (Mandelic Acid, Tranexamic Acid, Glycolic Acid, Lactic Acid Salicylic Acid) are known for brightening and resurfacing the skin while combatting breakouts and generally improving skin tone. While all of these acids are highly effective to treat hyperpigmentation, mandelic acid and tranexamic acid are most commonly considered the best options for treating melasma.
Sunscreen is like a cocoon that protects your skin from further damage and prevents more dark spots from developing during the hyperpigmentation treatment process. Apply sunscreen (with at least SPF 30) every morning for eternity to keep your skin evenly toned, healthy and glowy.

How To Get Rid of Hyperpigmentation: Natural Remedies
-
Aloe Vera
-
Apple Cider Vinegar
-
Calendula Oil
-
Lemons & Citrus Fruits
-
Turmeric
Aloe vera contains aloin, a depigmenting agent, which breaks down excess melanin and lightens skin to serve as a natural remedy to treat hyperpigmentation. It also helps combat acne, soothes eczema flare-ups and mitigates the effects of other minor skin trauma (like burns) to prevent future post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation patches from forming.
Calendula oil has been clinically proven to decrease melanin concentration in the skin (likely due to its high flavonoid content). The botanical extract also helps boost collagen production and offers some protection against UVB rays and future sun damage (equivalent to SPF 14) to amplify your sunscreen’s main benefits.
Zensa Healing Cream combines medicinal-grade calendula oil (and grapefruit essential oil, which is rich in melanin-fighting vitamin C) with aloe vera and other skin-nourishing ingredients like sunflower seed oil, avocado oil and shea butter to minimize acne scarring, soothe eczema flare-ups and boost collagen production for calmer and well-hydrated skin. These antioxidant-rich ingredients help reduce inflammation, are known to help with fading dark spots (shea butter is another effective natural remedy for hyperpigmentation) and prevent future skin discolouration. Here’s everything to know about Zensa Healing Cream.

Everyday kitchen staples like apple cider vinegar, lemons and other citrus fruits can potentially reduce hyperpigmentation, thanks to their acetic acid and vitamin C contents, respectively. Remember to always dilute these ingredients before applying them to the skin. This step is essential to prevent skin irritation. Turmeric is another popular home remedy used to treat hyperpigmentation. It helps decrease melanin production and has anti-inflammatory properties to calm eczema flare-ups and acne to prevent future scarring or other dark spots associated with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
How To Get Rid of Hyperpigmentation: Cosmetic Treatments
-
Microneedling
-
Chemical Peels
-
Microdermabrasion
-
Dermabrasion
Microneedling (collagen-induction therapy) is a cosmetic treatment that uses a derma roller containing several tiny needles to puncture the top layer of your skin. It’s like a strength-training exercise for your skin barrier. The procedure involves your expert creating a series of controlled injuries to develop micro-tears (tiny wounds) throughout your complexion and triggers the skin’s wound-healing response. This process stimulates collagen production to increase cellular turnover and improve the skin barrier’s resilience to treat uneven skin texture, brighten skin tone, provide anti-aging effects and reverse sun damage. Some benefits of microneedling include its ability to significantly reduce the appearance of acne scars, sun damage and generally improve all types of hyperpigmentation.
Chemical peels use exfoliating acids (AHAs, BHAs, salicylic acid) to slough off the top layer of dead skin cells to break up and remove excess melanin from your complexion. This process encourages cellular turnover to unveil a fresh layer of more even-toned skin. While effective, be extra cautious when considering getting a chemical peel if you have a darker complexion or black skin. Intense treatments like chemical peels are most likely to cause additional post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in individuals who naturally have higher melanin levels in their skin.
Microdermabrasion and dermabrasion are professional cosmetic treatments that use a physical exfoliant to remove the top layer of skin. Both procedures are performed using a drill-like handheld tool in an office setting. Microdermabrasion is designed for superficial scars, while dermabrasion penetrates deeper into the skin for faster results. Dermabrasion is typically only recommended for individuals with fairer complexions. Microdermabrasion is considered suitable for all skin types. Always consult with your dermatologist to determine which cosmetic treatment option(s) is best for your skin type, sensitivities and specific needs.
