Your Ultimate Skincare Guide to Heal Dry, Itchy Skin
Your Ultimate Skincare Guide to Heal Dry, Itchy Skin
Dehydrated skin can create considerable distress, especially chronic or left untreated. While usually harmless, dry, itchy skin can be caused by factors like seasonal weather changes, sun exposure, over-exfoliation, chronic inflammatory skin conditions (like eczema) and more. Regardless of the specific cause, dry skin results from a damaged skin barrier. The skin barrier, also called the stratum corneum, is made up of two elements: skin cells (called corneocytes) and lipids (which bind these skin cells together). The stratum corneum is responsible for helping retain moisture and preventing transepidermal water loss to keep your skin hydrated.
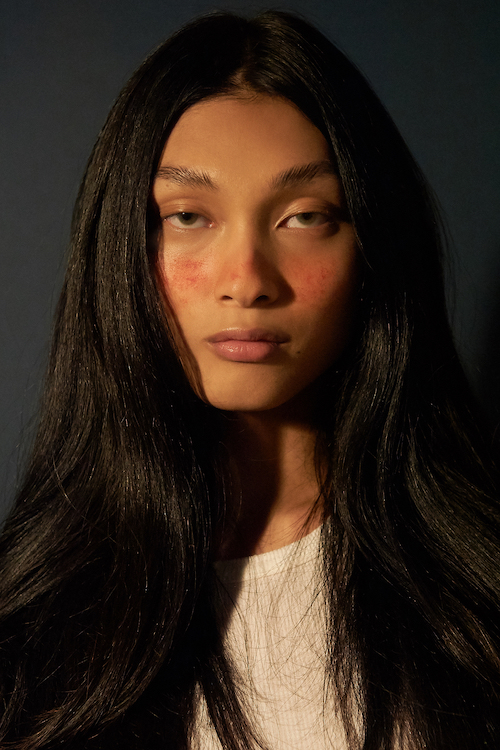
Skin barrier dysfunction occurs when the skin is stripped of its natural oils, leaving you with a weakened or compromised lipid barrier. Some signs of a weakened lipid and skin barrier include rough or flaky patches, redness, dryness, swelling, irritation, itchiness, rough skin texture and persistent bumps or breakouts. Dry skin has a thinner texture than plump, well-hydrated skin. This thinner skin texture is more prone to cracking and irritation, potentially leading to bleeding or an infection.
From the inside out, a well-nourished complexion is essential for skin health. Hydrated skin looks smoother, is more resilient, has a more even texture, feels softer to the touch, and provides a youthful glow.
Read on to learn more about what causes and how to heal dry, itchy skin.

Causes of Dry, Itchy Skin
Dry, itchy skin can be caused by changes in the temperature or humidity (especially in the winter), sunburns, insect bites, an allergic reaction, a vitamin D deficiency, or an inflammatory condition, such as eczema, rosacea or psoriasis.
Refine Your Skincare Routine
The products you use can make or break your skin’s suppleness and vitality. Strong facial cleansers or body washes can dry out the skin by stripping it of its natural oils. Regardless of the cause of your dry, itchy skin, there are certain products you’ll want to remove and incorporate into your routine. Always use fragrance-free products to avoid chemicals that could easily irritate your skin. Any type of retinoids – such as retinol – typically should not be used on dry, itchy skin. Never use retinoids on inflammatory patches, from eczema or rosacea, sunburns, hives or cold sore-prone skin. Retinoids increase cellular turnover, which can cause “retinol burn” and increase uncomfortable symptoms like flaky patches and dry, itchy skin. Only use retinol on dry skin when your skin barrier is not too compromised. When using retinol to repair dry, itchy skin apply an OTC retinol with a low-dose concentration and pair it with humectants (water-attracting ingredients) like hyaluronic acid, glycerin, glycolic or lactic acid.

Incorporate humectants like hyaluronic acid, aloe vera or AHAs (alpha hydroxy acids) like lactic or glycolic acid, into your everyday routine. Humectants attract water from the outside environment and deeper layers of the skin to the epidermis (top layer of the skin) helping to increase your complexion’s overall hydration. These ingredients help nourish and repair your skin barrier without clogging your pores, making them suitable for all skin types (including dry patches on combination or oily skin).
Emollients, like shea butter, nourish and soothe dry, itchy skin. Ceramides (fatty acids naturally found in the skin), moisturize the skin to repair the skin barrier, protect against irritants and infection and improve the skin’s resiliency to actives in other skincare products. Shea butter hydrates dry skin, softens dry patches and soothes itchiness caused by allergic reactions, insect bites, sunburns, rashes, eczema, psoriasis and parched, cracked skin.

Stay Chemical-Conscious
Harsh chemicals, in any products that touch your skin, can cause contact dermatitis (a red, scaly rash that leaves you with dry, itchy skin). Contact dermatitis can be caused by soaps, moisturizers, hair care products, makeup, detergents, certain plants and more. It inflames your skin and can look similar to eczema (atopic dermatitis). However, contact dermatitis is a temporary – not chronic – condition. Once you stop using the product causing the reaction, you usually can calm the swelling and irritation by using a steroid cream or ointment. To prevent contact dermatitis, avoid any skincare, makeup, haircare or laundry products containing fragrances, preservatives or any strong chemicals. Look for the most natural and gentle products possible, especially if you already have sensitive skin.
Some home remedies for dry, itchy skin include colloidal oatmeal baths, coconut oil, petroleum jelly (Vaseline) or extra virgin olive oil.
Heighten The Humidity
Extreme temperatures easily anger your skin. The skin traps water from the moisture in the air to keep the epidermis hydrated. However, in the winter dry skin is common due to a drop in humidity – both outside and indoors. The cold, brisk outdoors are often accompanied by high heat inside that further dries out the air. This low moisture level can cause transepidermal water loss and a weakened skin barrier. Use a humidifier at home to rehydrate the skin. Limit the time spent submerging your skin in water. Keep your showers short. Moisturize your entire body afterward. Always use lotion after washing your hands to avoid cracking or skin irritation.

Remain Neutral
Balance is essential to healing dry, itchy skin. When showering or washing your hands (or face), always try to use lukewarm water. Steaming hot water will only further dry out the moisture barrier. Moisturize daily to provide enough hydration to the skin without clogging your pores or irritating your complexion.
Healthy lifestyle habits can significantly benefit your skin. Maintain a balanced diet that includes dark, leafy greens, berries, citrus fruits, oatmeal, avocado, sweet potatoes, tomatoes, nuts and seeds. These nutrient-dense foods are all either water-rich or contain a high amount of healthy fats to lock in moisture and replenish the lipid barrier from within.
Unmanaged stress also can show up on your skin. Stress is one of the most common triggers for eczema flare-ups, which can cause uncomfortable swelling, itching, redness and dry, leathery skin. Releasing higher amounts of cortisol, the hormone responsible for stress-regulation can make your skin produce excess oil (a common cause of acne) and make it more difficult for your skin to recover from irritants or other types of skin damage (moisture loss, sun exposure, etc.). Find a routine that works for you with activities like meditating, exercise, journaling, yoga and reading to center yourself and manage your daily mood.
Prioritize Hydration
Drinking enough water is essential for hydrated skin and your overall wellbeing. Aim to drink around your weight in ounces of water every day. Eat water-rich foods (namely fresh produce or soups) and drink non-caffeinated or green tea to further increase your daily water intake.
Apply a nourishing lotion to hydrate and heal your skin. Zensa Healing Cream contains medicinal ingredients like calendula oil and grapefruit oil to treat various causes of dry, itchy skin, including seasonal dryness, allergic reactions, rashes, eczema and wound healing (especially during the tattoo after-care process). Calendula oil hydrates the skin (thanks to its calendic and linoleic fatty acid content) and contains anti-inflammatory properties to help restore the skin barrier. Grapefruit oil is rich in vitamin C, which has been clinicially proven to help reduce skin inflammation.
Zensa Healing Cream also contains nourishing ingredients, such as hyaluronic acid, aloe vera, shea butter and glycerin, among others for hydration and calm inflammation to leave you with smoother, healed skin.

Supplement Vitamin D
Vitamin D deficiency is a cause of dry, itchy skin that can easily fly under the radar. Sufficient vitamin D is essential to maintain a healthy skin barrier. When your vitamin D levels drop too low (either due to genetics or lifestyle choices), you will likely experience severely dry skin. Vitamin D is rich in antioxidants, which help nourish and repair the skin barrier, reduce inflammation (including acne) and can help relieve symptoms of conditions like eczema, psoriasis and rosacea.
Get your vitamin D levels checked to confirm whether a nutrient deficiency could be causing your dry skin. Restore your vitamin D levels with a daily supplement and attempt to get at least 10 minutes of sunlight on your skin every day (always wear sunscreen). These daily practices will improve both your skin and your mood.

Be Gentle
Compassion for your complexion is essential to healing inflammation or dry, itchy skin. Practices like over-exfoliation can be too abrasive, leaving you with a weakened skin barrier and a raw, irritated complexion. If your skin is already extremely dry or itchy, hold off on exfoliating your skin until you can rehydrate and heal your complexion. Use a gentle cleanser, moisturizer and nourishing serum (such as a hyaluronic acid serum) to rehabilitate your skin. Once the skin barrier is restored, ease back into a regular exfoliation routine. Exfoliate 1-3 times a week for optimal results.
Also, be mindful of the fabrics that regularly interact with your skin. Choosing clothing and sheets made from soft, breathable fabrics like cotton, linen, silk, hemp or cashmere will help you feel more comfortable throughout the day as you heal your dry, itchy skin.
Always remember that repairing overworked skin is a long-term endeavor. Stay consistent with your skincare routine, nutrition and positive lifestyle habits. Over time, your hard work will pay off and leave your complexion soft and glowing, so you feel comfortable in your own skin.
